Introduction
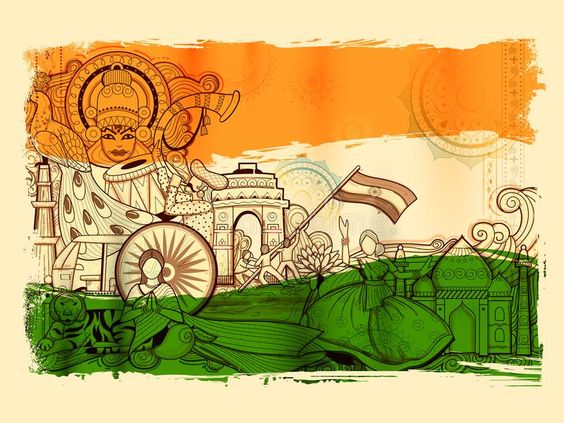
India, a land of myriad cultures, languages, religions, and traditions, stands as a testament to the marvels of human diversity. The concept of diversity in India transcends beyond the conventional understanding of ethnic, racial, or linguistic differences. It encompasses an intricate web of regional, historical, and social complexities that have shaped the nation’s identity. This article delves into the multifaceted dimensions of diversity in India, examining its profound influence on children, the repercussions it carries, its primary cause, historical perspectives, and ultimately, celebrating its significance in shaping India’s pluralistic ethos.

Various Sorts of Diversity in India
1.1 Cultural Diversity:
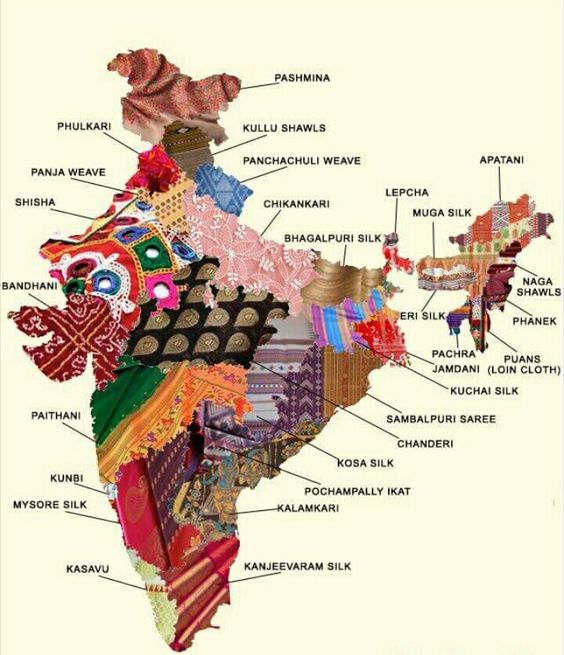
India’s cultural mosaic is a rich tapestry woven over centuries, adorned with the customs, art forms, music, dance, and festivals that vary across regions. Each state embraces its unique heritage, further divided into sub-cultures, making India a treasure trove of cultural diversity.
1.2 Linguistic Diversity:
The linguistic diversity in India is awe-inspiring, boasting an estimated 19,500 languages, including 22 officially recognized languages. This linguistic plurality not only reflects the people’s identities but also showcases their ability to communicate across linguistic barriers.

1.3 Religious Diversity:
India stands as a land where various religions coexist harmoniously. Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, Jainism, and others form the fabric of religious pluralism, shaping the ethos of tolerance and inclusivity.
1.4 Socio-economic Diversity:
India’s diversity is also reflected in its socio-economic landscape. There exist disparities in wealth, education, and access to resources between rural and urban areas and across different communities.
Influence of Diversity on a Child in India
Diversity plays a pivotal role in a child’s upbringing in India. From an early age, children are exposed to a plethora of cultures, languages, and traditions, fostering a sense of curiosity and tolerance. They learn to respect and appreciate different perspectives, laying the foundation for a harmonious and inclusive society.
Multilingualism allows children to develop better cognitive skills, adaptability, and empathy, while exposure to diverse art forms and traditions nurtures their creativity and cultural awareness.
Positive Consequences of Diversity in India
3.1 Cultural Vibrancy:
India’s diversity contributes to a vibrant cultural landscape, boasting a diverse array of art, music, dance, and literature that enraptures the world.
3.2 Social Cohesion:
The coexistence of various communities fosters social cohesion, leading to a harmonious society where people learn to appreciate one another’s differences.
3.3 Tolerance and Acceptance:
Diversity encourages tolerance and acceptance, instilling a sense of unity amidst differences, ensuring India’s strength lies in its unity.
3.4 Innovative Potential:
The amalgamation of diverse perspectives nurtures innovation and problem-solving, leading to progress and growth in various sectors.
Negative Consequences of Diversity in India
4.1 Communal Tensions:
Diversity sometimes becomes a source of tension, leading to communal conflicts and violence.
4.2 Fragmentation of Identity:
With a multitude of identities coexisting, there is a risk of fragmentation, challenging the idea of a singular national identity.
4.3 Inequalities:
Socio-economic diversity can perpetuate inequalities, leading to disparities in opportunities and resources.
Primary Cause of India’s Diversity Today
The primary cause of India’s diversity lies in its historical legacy. Centuries of migration, invasions, and trade relations have led to the blending of various cultures and traditions. Moreover, the subcontinent’s vast geographical expanse, with diverse landscapes and climates, further contributed to the emergence of distinct regional identities.
Historical Perspectives of Diversity in India
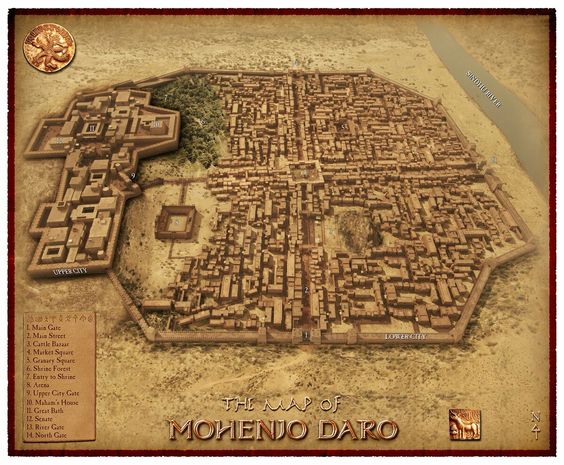
6.1 Ancient Civilizations:
India’s history dates back to ancient civilizations, such as the Indus Valley Civilization and the Vedic period, which laid the foundation for cultural diversity.
6.2 Invasions and Migrations:
Throughout history, India witnessed invasions by the Persians, Greeks, Mughals, and others, bringing in new cultures and religions that integrated with the indigenous ones.
6.3 Colonial Era:
The colonial rule by the British profoundly impacted India’s diversity, introducing western education, culture, and administrative structures.
Conclusion
India’s diversity is a testament to the resilience and openness of its people. It enriches the nation, offering a vibrant cultural landscape and fostering a spirit of unity in diversity. While diversity poses challenges, it also presents tremendous opportunities for growth, progress, and mutual respect.
Nurturing the positive aspects and addressing the negative consequences will enable India to preserve and celebrate its diverse heritage while marching confidently towards a more inclusive and harmonious future. As the world becomes more interconnected, India’s tapestry of diversity stands as a source of inspiration and admiration for global societies striving to embrace the beauty of human plurality.



